Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the practice of optimizing your website to improve its visibility and rankings in search engine results pages (SERPs). For beginners, understanding SEO fundamentals is essential for driving organic traffic, building online presence, and growing your business without relying solely on paid advertising.
What is SEO and Why is it Important?
Search Engine Optimization is the process of improving your website’s visibility in organic (non-paid) search results on platforms like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. The primary goal is to attract more qualified traffic to your website by ensuring it appears when people search for terms related to your business, products, or services.
SEO is crucial because:
30% of all mobile searches are location-related
78% of people who search for something nearby on their phones visit the business within a day
Higher rankings typically lead to more traffic, with most users clicking on the first few search results
Unlike paid advertising, organic traffic is “free” and provides consistent, long-term results
SEO builds trust and credibility, as users generally trust organic results more than ads
How Do Search Engines Work?
Understanding how search engines operate is fundamental to effective SEO. Search engines work through three primary functions:

1. Crawling
Crawling is the discovery process where search engines send out robots (called crawlers, bots, or spiders) to find new and updated content on the internet. These crawlers navigate by following links from one page to another, downloading web pages and analyzing their content.
2. Indexing
After crawling, search engines store and organize the discovered content in a massive database called an index. The index contains information about each page’s keywords, content type, freshness, and various signals that help determine relevance.
3. Ranking
When users perform a search, the search engine’s algorithm evaluates all relevant pages in the index and ranks them from most to least relevant based on hundreds of factors. The goal is to provide the most helpful and authoritative results for each query.
What Are the Main Types of SEO?
SEO consists of four main categories that work together to improve your website’s search performance:
Technical SEO
Technical SEO focuses on optimizing the technical aspects of your website to ensure search engines can crawl, index, and understand your content effectively. Key elements include:
Site architecture and URL structure – Creating logical, user-friendly navigation
Page speed optimization – Ensuring fast loading times across all devices
Mobile-friendliness – Implementing responsive design for mobile users
SSL certificates – Securing your website with HTTPS
XML sitemaps – Helping search engines discover your content
Robots.txt files – Controlling which pages search engines can access
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO involves optimizing individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic. This includes:
Keyword optimization – Using target keywords naturally in titles, headings, and content
Title tags and meta descriptions – Writing compelling, keyword-rich titles and descriptions
Header tags (H1, H2, H3) – Organizing content with proper heading structure
Internal linking – Connecting related pages within your website
Image optimization – Using descriptive file names and alt text
Content quality – Creating valuable, comprehensive content that serves user intent
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO encompasses activities performed outside your website to improve search rankings and build authority. Primary tactics include:
Link building – Earning high-quality backlinks from reputable websites
Social media engagement – Building brand awareness and social signals
Brand mentions – Getting your business mentioned on other websites
Guest blogging – Writing content for other relevant websites
Local citations – Listing your business in online directories
Content SEO
Content SEO focuses on creating and optimizing content that satisfies user search intent while incorporating relevant keywords naturally. This involves:
Content strategy development – Planning content around target keywords and user needs
Topic authority building – Creating comprehensive content on your expertise areas
User experience optimization – Making content easily readable and engaging
Regular content updates – Keeping information fresh and relevant
How to Do Keyword Research?
Keyword research is the foundation of successful SEO, helping you understand what terms your target audience uses when searching for your products or services.
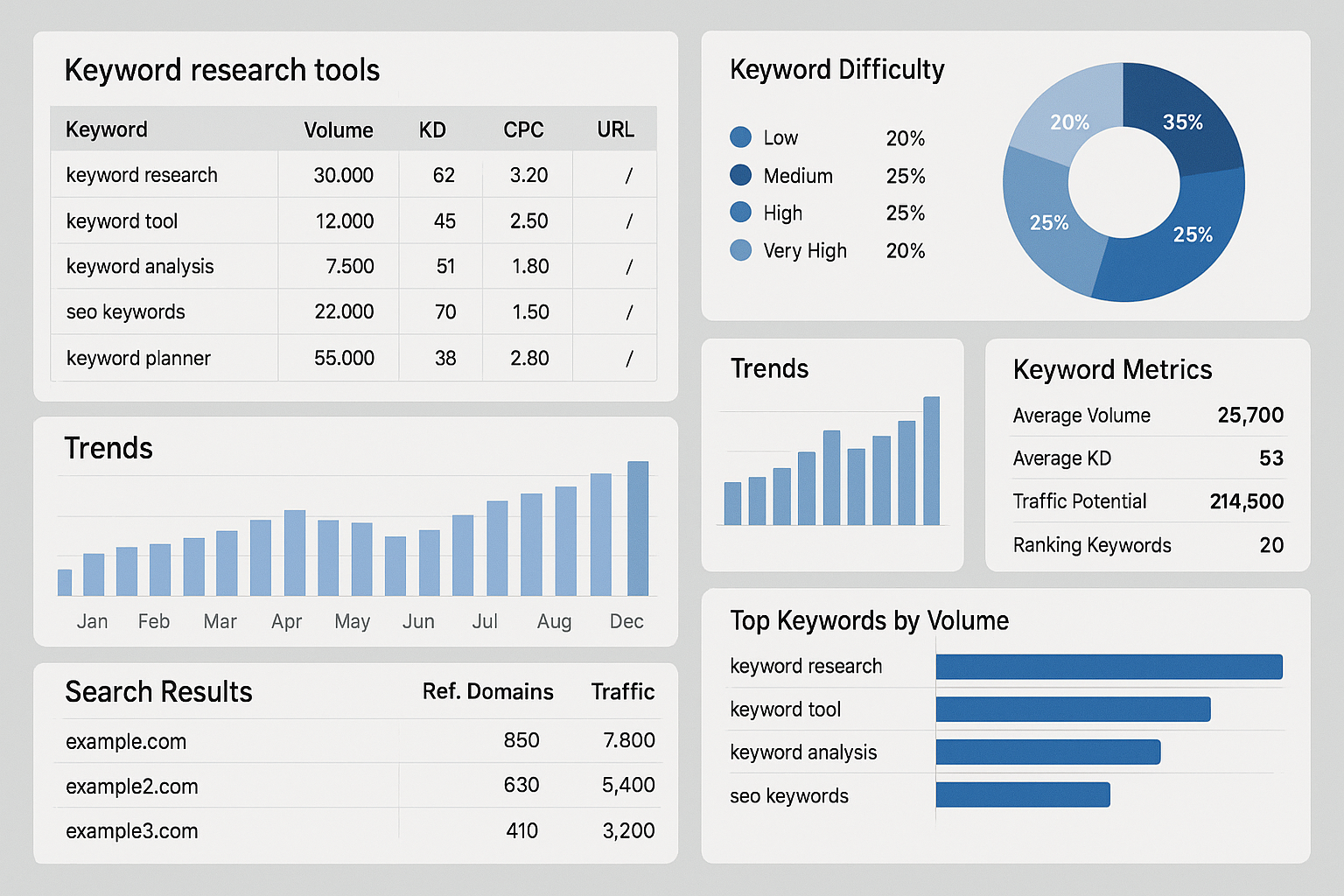
Understanding Keyword Types
Short-tail keywords are broad terms with high search volume but intense competition (e.g., “coffee”). Long-tail keywords are more specific phrases with lower volume but higher conversion potential (e.g., “best organic coffee beans for espresso”).
Search intent categories include:
Informational – Users seeking information (“how to make coffee”)
Navigational – Users looking for specific websites (“Starbucks website”)
Commercial – Users researching products (“best coffee makers”)
Transactional – Users ready to purchase (“buy coffee beans online”)
Keyword Research Process
Brainstorm seed keywords – Start with broad topics related to your business
Use keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs
Analyze search volume and difficulty – Look for keywords with decent search volume but manageable competition
Study competitor keywords – See what terms your competitors rank for
Focus on user intent – Ensure keywords align with what users actually want
Best Practices for Keyword Research
Target keywords with clear search intent that matches your content goals
Consider keyword difficulty scores – beginners should focus on easier keywords initially
Look for question-based keywords that you can answer comprehensively
Use keyword variations and synonyms to avoid over-optimization
Prioritize local keywords if you serve specific geographic areas
What is On-Page SEO and How to Optimize It?
On-page SEO involves optimizing elements directly on your website pages to improve search engine rankings and user experience.
Essential On-Page SEO Elements
Title Tags
Create unique, descriptive titles under 60 characters that include your target keyword near the beginning. Example: “Complete Beginner’s Guide to SEO in 2025 | Your Brand”
Meta Descriptions
Write compelling descriptions under 160 characters that summarize your content and encourage clicks. Include your target keyword naturally while focusing on user value.
Header Tags (H1, H2, H3)
Structure your content with clear headings that help both users and search engines understand your page organization. Use your main keyword in the H1 tag and related terms in subheadings.
URL Structure
Create clean, descriptive URLs that include keywords and are easy to understand. Use: /seo-beginners-guide-2025 instead of /page?id=12345
Internal Linking
Link to relevant pages within your website using descriptive anchor text. This helps search engines understand your site structure and keeps users engaged longer.
Image Optimization
Use descriptive filenames and alt text for images. Compress images for faster loading and include relevant keywords when appropriate.
Content Optimization Strategies
Include target keywords naturally throughout your content, especially in the first 100 words
Write for users first – create valuable, comprehensive content that answers their questions
Use semantic keywords and related terms to demonstrate topic authority
Optimize content length based on what ranks well for your target keywords
Improve readability with short paragraphs, bullet points, and clear formatting
What is Off-Page SEO and Link Building?
Off-page SEO refers to optimization activities performed outside your website that influence your search engine rankings. The most important off-page factor is building high-quality backlinks from other reputable websites.
Link Building Strategies
Guest Blogging
Write valuable content for relevant websites in your industry. This allows you to demonstrate expertise, reach new audiences, and earn quality backlinks to your site.
Resource Page Link Building
Find websites with resource pages listing helpful links in your industry. Reach out to suggest your content as a valuable addition to their list.
Broken Link Building
Identify broken links on relevant websites and offer your content as a replacement. This provides value to the website owner while earning you a backlink.
Digital PR and Outreach
Create newsworthy content, conduct original research, or offer expert commentary to earn mentions and links from news sites and industry publications.
Building Domain Authority
Focus on link quality over quantity – one link from a highly authoritative site is worth more than dozens from low-quality sources. Diversify your link profile with links from various types of websites including blogs, news sites, and industry directories.
Monitor your backlink profile using tools like Google Search Console or Ahrefs to identify and disavow harmful links that could hurt your rankings.
Technical SEO Basics for Beginners
Technical SEO ensures search engines can easily crawl, index, and understand your website. While it might seem complex, focusing on these fundamental areas will significantly improve your SEO foundation.
Website Speed Optimization
Page speed is a crucial ranking factor and user experience element. Optimize images by compressing them and using modern formats like WebP. Minimize HTTP requests by combining files and removing unnecessary plugins. Use browser caching to store frequently accessed files locally on users’ devices.
Mobile Optimization
With mobile-first indexing, Google primarily uses your mobile site for ranking. Implement responsive design that adapts to all screen sizes. Test your site on various mobile devices and use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool to identify issues.
Site Architecture
Create a logical site structure that makes it easy for users and search engines to navigate. Use clear navigation menus with descriptive labels. Implement breadcrumb navigation to show users their location within your site. Ensure no page is more than 3-4 clicks from your homepage.
Security and HTTPS
Google considers HTTPS a ranking signal. Install an SSL certificate to encrypt data between your server and users’ browsers. This not only improves security but also builds trust with visitors who see the lock icon in their browser.
Local SEO Fundamentals
Local SEO helps businesses with physical locations or those serving specific geographic areas appear in location-based searches.
Google Business Profile Optimization
Claim and verify your Google Business Profile (formerly Google My Business). Complete all profile sections including business hours, phone number, address, and description. Add high-quality photos of your business, products, and services. Encourage customer reviews and respond to them professionally.
Local Citations and NAP Consistency
Ensure your Name, Address, and Phone number (NAP) are consistent across all online directories and citations. Submit to relevant local directories like Yelp, Yellow Pages, and industry-specific listings. Monitor and update citations regularly to maintain accuracy.
Local Content and Keywords
Create location-specific content that serves your local audience. Use local keywords like “coffee shop in [city name]” throughout your website. Write about local events, news, and community involvement to demonstrate local relevance.
SEO Analytics and Tracking
Measuring your SEO performance is essential for understanding what works and identifying areas for improvement.
Essential SEO Tools
Google Search Console is a free tool that shows how Google sees your website. Monitor your search performance, identify crawling issues, and track keyword rankings. Google Analytics 4 provides insights into user behavior, traffic sources, and conversion tracking.
Third-party tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, or Moz offer additional features like competitor analysis, keyword research, and backlink monitoring. SEO audit tools like Screaming Frog help identify technical issues.
Key Metrics to Monitor
Organic traffic – The number of visitors from search engines
Keyword rankings – Your position for target keywords
Click-through rates (CTR) – Percentage of users who click your results
Bounce rate – Users who leave after viewing one page
Conversion rate – Visitors who complete desired actions
Regular SEO Audits
Perform monthly SEO audits to identify technical issues, content gaps, and optimization opportunities. Track ranking changes and investigate significant fluctuations. Monitor your backlink profile for new links and potential issues.
Common SEO Mistakes to Avoid
Understanding common pitfalls can save you time and prevent ranking penalties.
Content-Related Mistakes
Keyword stuffing – Overusing keywords unnaturally in content makes it unreadable and can trigger penalties. Duplicate content – Publishing similar content across multiple pages confuses search engines and dilutes your rankings.
Thin or low-quality content fails to provide value to users and won’t rank well. Ignoring user intent by optimizing for keywords without understanding what users actually want leads to poor performance.
Technical Mistakes
Slow loading speeds frustrate users and hurt rankings. Poor mobile optimization ignores the majority of users who browse on mobile devices. Broken links create poor user experiences and waste crawl budget.
Conflicting signals like using noindex tags with canonical tags send mixed messages to search engines. Missing or poorly optimized meta tags waste opportunities to attract clicks from search results.
Strategic Mistakes
Focusing only on traffic volume instead of qualified, converting traffic misaligns with business goals. Neglecting local SEO when serving geographic markets misses valuable opportunities. Not staying updated with algorithm changes and best practices leads to outdated strategies.
Creating an SEO Strategy for Success
Building a comprehensive SEO strategy ensures all your optimization efforts work together toward common goals.
Setting SEO Goals
Define clear, measurable objectives that align with your business goals. Examples include increasing organic traffic by 30% in six months or ranking in the top 3 for specific keywords. Focus on metrics that drive business value like conversions and revenue rather than just traffic.
Content Strategy Development
Conduct a content audit to identify gaps and opportunities in your existing content. Create a content calendar that regularly publishes valuable content around your target keywords. Focus on building topical authority by covering subjects comprehensively rather than randomly targeting keywords.
Implementation Timeline
Phase 1 (Months 1-2): Fix technical issues, optimize existing content, and set up tracking tools. Phase 2 (Months 3-6): Create new content, build links, and refine your strategy based on performance data. Phase 3 (Months 6+): Scale successful tactics, expand keyword targets, and continuously optimize based on results.
Future of SEO in 2025 and Beyond
SEO continues evolving with technological advances and changing user behavior. AI and machine learning increasingly influence how search engines understand and rank content. User experience signals like Core Web Vitals become more important ranking factors.
Voice search optimization grows in importance as more users search via smart speakers and mobile assistants. E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) remains crucial for content ranking, especially in competitive niches.
Video and visual search continue expanding, requiring optimization of multimedia content. Local and mobile-first indexing emphasize the importance of location-based and mobile-optimized content.
SEO success in 2025 requires focusing on user value, technical excellence, and building genuine authority in your field. By mastering these fundamentals and staying updated with industry changes, you’ll build a strong foundation for long-term search engine success.
Remember that SEO is a long-term strategy that requires patience and consistency. Start with the basics covered in this guide, implement changes systematically, and continuously monitor your progress. With dedication and proper execution, you’ll see meaningful improvements in your search engine rankings and organic traffic growth.


