What Happened on July 19, 2024?
On July 19, 2024, a faulty configuration update from CrowdStrike’s Falcon sensor software triggered blue screen errors and boot loops on approximately 8.5 million Windows systems worldwide, disrupting Azure cloud services and Microsoft 365 apps—including Outlook, Teams, and OneDrive.
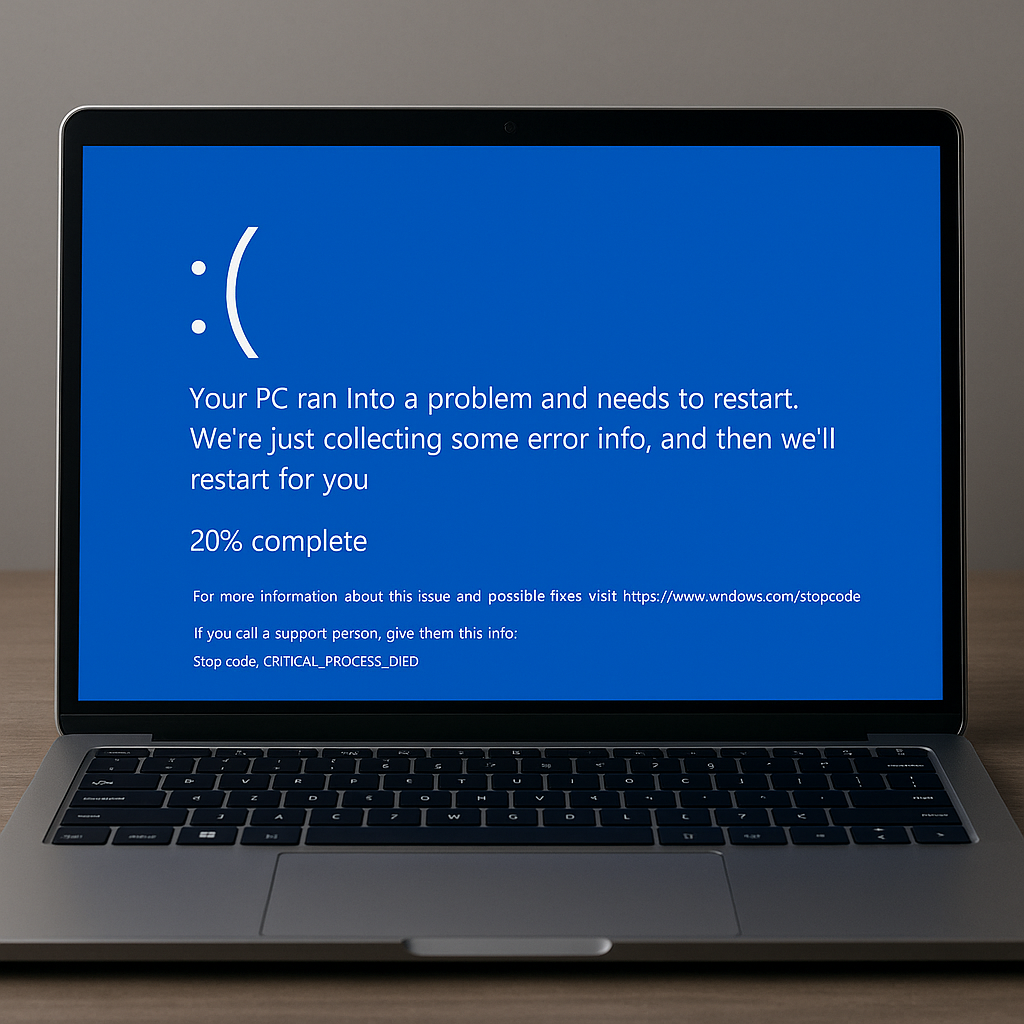
What Caused the Outage?
A CrowdStrike update to “Channel File 291” contained an out-of-bounds memory read bug. Because Falcon runs at the kernel level (ring 0), the fault forced a system crash (BSOD) on Windows 10 and 11 machines with the sensor installed.
Which Services Were Affected?
Microsoft 365 (Outlook, Teams, SharePoint)
Azure Virtual Machines and storage-dependent services
Windows 365 Cloud PCs
Third-party platforms reliant on Azure (e.g., airline check-in systems)
How Did It Unfold (Timeline UTC)?
| Time | Event |
|---|---|
| 04:09 | Faulty update released by CrowdStrike |
| 05:27 | CrowdStrike reverts the update |
| 06:48 | Azure VMs begin crashing; Google Compute Engine reports issues |
| 07:15 | Google identifies CrowdStrike update as cause |
| 09:45 | CrowdStrike CEO confirms fix deployed; outage not a cyberattack |
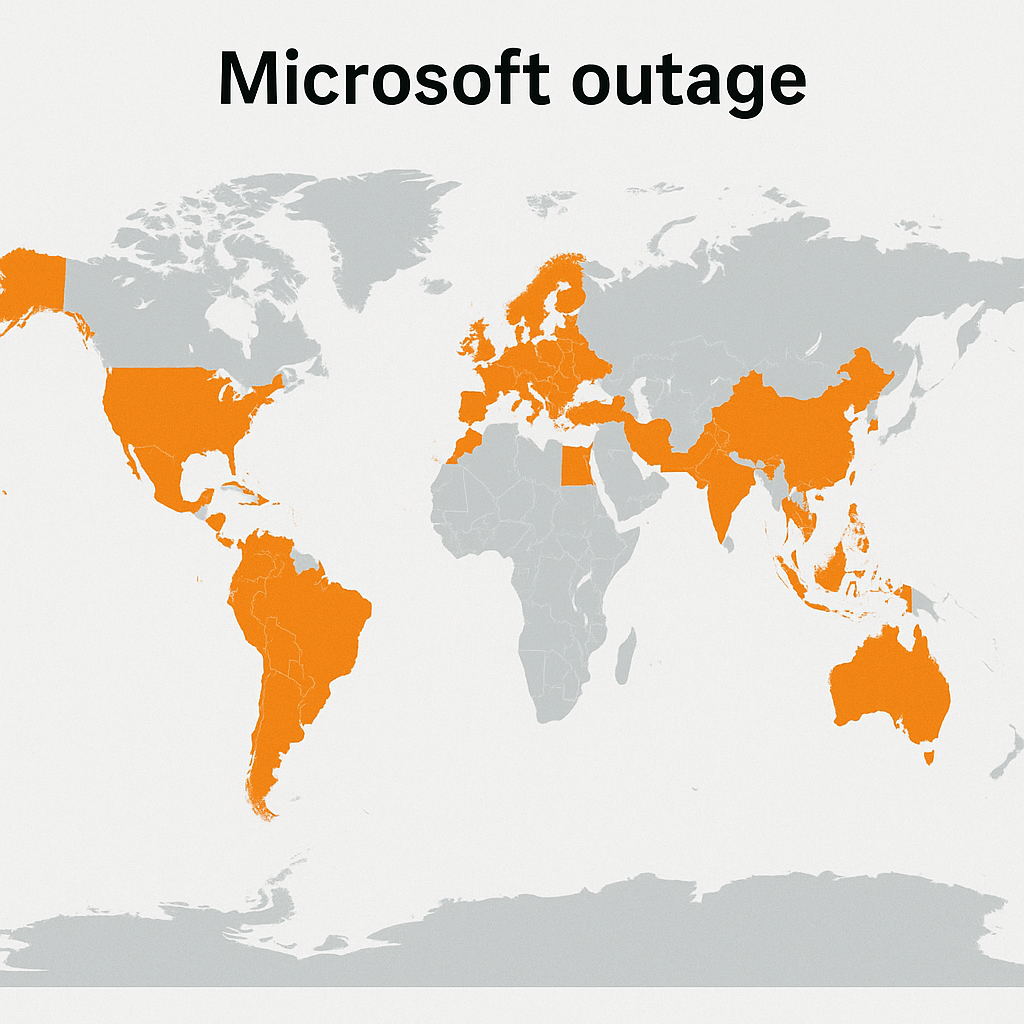
What Was the Global Impact?
Outages spanned business hours in Oceania and Asia, early morning in Europe, and midnight in the Americas, affecting airlines, banks, healthcare, government services, and retail. Financial losses exceeded US$10 billion globally.
Who Was Affected by Industry?
| Industry | Examples of Impact |
|---|---|
| Air Transport | Over 5,000 flights cancelled; Delta alone cancelled 7,000 flights, costing $550 million in losses |
| Finance | Major banks (Chase, RBC) and stock exchanges (LSE, SGX) faced service disruptions |
| Healthcare | Hospitals paused non-urgent procedures due to inaccessible patient records |
| Government Services | 911 call centers in multiple US states experienced outages; DMV operations disrupted |
| Retail | POS systems at supermarkets and coffee chains went offline, forcing cash-only transactions |
How Was the Outage Resolved?
Automated Remediation: Reverting the faulty update and rebooting connected machines
Manual Fixes: Booting into Safe Mode or Windows Recovery to delete corrupted driver files and reapply the correct channel file
Backups: Restoring system images created before July 18, 2024
What Lessons Were Learned?
Staggered Rollouts: Avoiding “all-at-once” updates to critical infrastructure
Robust Testing: Incorporating regression tests for legacy configurations
Ecosystem Collaboration: Real-time coordination among Microsoft, CrowdStrike, AWS, and GCP for rapid mitigation
Frequently Asked Questions
Was This a Cyberattack?
No. CrowdStrike and Microsoft confirmed it was a software defect in a legitimate update, not a security breach.
Which Regions Were Least Affected?
China, Russia, and Iran saw minimal disruptions due to self-sufficient IT infrastructures and limited adoption of US-based software.
How Can Organizations Prepare?
Implement multi-phase deployments, maintain offline backups, and establish rapid-response teams to isolate and remediate faults in critical updates.
This guide equips IT professionals, business leaders, and general users with the essential facts, impact analysis, and recovery steps following the July 19, 2024 Microsoft outage.